What Are the Advantages of Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology significantly transforms various industries, including finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and real estate. What makes it revolutionary? Well, it is a decentralized and immutable ledger that enables secure and transparent transactions. No wonder people often say it is all about cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin; the truth is that blockchain applications extend far beyond digital currencies.
What Is Blockchain?

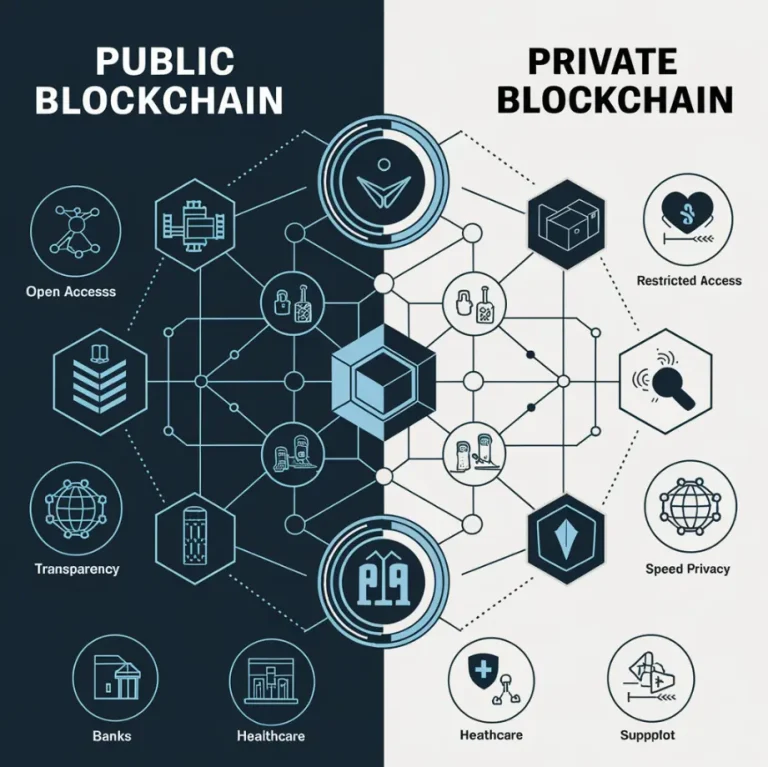
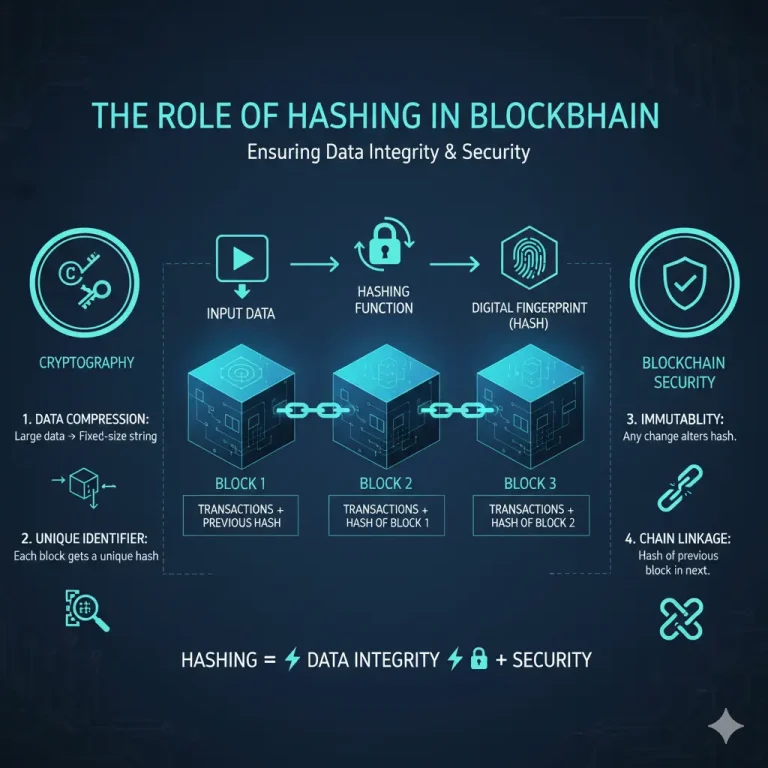
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that enables secure, transparent, and tamper-resistant data storage across a network of computers. Every “block” in the chain includes a list of transactions, and once the block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or removed. Hence, all transactions survive as permanent and verifiable records. Unlike conventional databases, which are managed from a central point by a single entity, blockchain operates on a decentralized network.
Therefore, no individual or party is allowed to interfere with or exert control over the entire system; generally, it is more democratized and less susceptible to fraud. If you’re curious about specific design considerations for blockchain in various applications, it would be advisable to explore knowledge about private versions of public blockchains, which offer increased control and privacy without compromising most of the benefits of blockchain technology.
Importance of Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain technology is significant due to its ability to address some of the challenges facing the modern digital world. Here are the basic reasons:
- Decentralized: Blockchain technology eliminates corruption, censorship, and unprecedented failures by eliminating the need for a central authority.
- Trust and Transparency: All participants on the blockchain can see every single transaction, which fosters trust and accountability.
- Security: Blockchain’s use of cryptographic techniques ensures the security of data, making tampering impossible.
- Efficiency: Blockchain enhances the process by eliminating intermediaries, thereby reducing costs and facilitating faster transactions.
In a world facing the growing threat of data breaches and fraud, blockchain offers a viable and unique solution for information security and building trust.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology for Business:
Blockchain technology is not a fancy tool for techies but a very powerful asset for businesses in many sectors. Here are some other key ones:
- Lower Costs: Reducing operational costs by eliminating intermediaries and automating processes.
- Better Supply Chain Management: The goods are tracked, thus allowing real-time tracing, so there is transparency and efficiency in supply chains.
- Higher Customer Trust: Empowered relationships with customers go through transparency and security.
- Faster Transactions: Blockchain provides near-instantaneous transactions anywhere in the world, thereby boosting cash flow and customer satisfaction.
- Regulatory Compliance: Thanks to the immutability feature of blockchain, it becomes more manageable for organizations to comply with regulations and keep their records intact.
5 Benefits of Blockchain Technology:
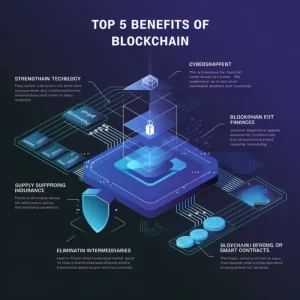
Now, it is time to discuss the importance and business applications of blockchain technology, before exploring the top 5 benefits of this revolutionary technology.
Security through CyberSecurity:
There are many important aspects of blockchain technology, one of which is its ability to enhance cybersecurity. Traditional systems often utilize centralized databases that are susceptible to hacking and data breaches. The blockchain obtains techniques that use high levels of cryptography to secure data. Every transaction is encrypted and linked to its predecessor, thus creating an almost impossible chain to alter. It is decentralized, so there is no single point of failure; this, therefore, would be considered a great solution for the protection of sensitive information.
So what is a plus point for introducing this type of technology in terms of cybersecurity? It is, in short, a tamper-proof system, which significantly minimizes risks against fraud and unauthorized access.
Transparent:
Another key benefit resultant from blockchain is transparency. Every transaction that occurs on a blockchain is open to every participant in the network. Such transparency means that all parties have the same information, and hence, there is less chance of a dispute or misunderstanding. For a network like that of supply chain management, it implies keeping stakeholders informed about goods movement in real-time, creating accountability and trust in the network.
Instant Traceability:
Instant traceability is what this piece of technology changes for industries whose work depends on closely following products or transactions. As an illustration, blockchain could allow the tracing of ingredient origins in its association with the food industry, ensuring food safety and quality. Here, each step in the production chain is recorded by the blockchain, giving an audit trail that cannot be concluded otherwise. This would create an even more trustworthy environment for improving compliance with regulatory requirements.
Improved Efficiency and Speed:
Most of the outdated transaction systems have a few or more intermediaries that cause the delay while increasing the transaction costs. Blockchain removes those extra costs by facilitating peer-to-peer interaction, which speeds up the time of transactions and lowers operational costs for the involved industries. As an example, it points out that a cross-border payment can take several days, but with blockchain technology, it can be done within a few minutes.
Efficiency means automating and simplifying complex, time-consuming processes through cost-saving and better resource utilization while improving overall productivity.
Automation:
Automating processes is now possible through combining blockchain technology with smart contracts that execute themselves when conditions are fulfilled. A smart contract refers to a self-executing agreement, including code directly into the terms. With smart contracts, when some predefined conditions are met, the contract executes without further action required. This, in particular, is interesting in insurance, where claims can be submitted and paid via automated system lines.