What is a Private Version of a Public Blockchain?
Blockchain technology has completely changed our understanding of security, data, transparency, and decentralization. While well-known public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum dominate the spotlight, another version is gaining attention: what is a private version of a public blockchain But what exactly is it, and how is it different from its public counterpart? Let’s dive into this interesting topic to uncover the private blockchains’ unique features and benefits. Explore the Top 10 Blockchain Companies making significant strides in the industry.
What is Blockchain?

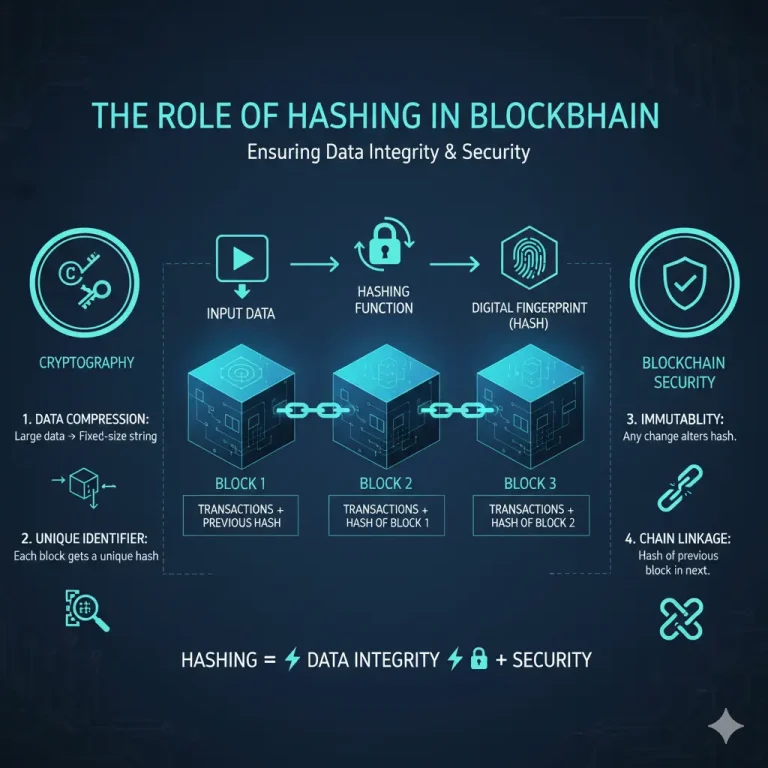
Before looking at the private variants of public blockchains, first, a look needs to be given at what blockchain exactly is. A blockchain is a digitized ledger list that records all transactions transparently and securely one that cannot have any alterations. Every block within it contains some transactions.
Public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are permissionless. Permissionless means anyone can join the network, transact, or even validate blocks-a process called mining. But this comes with challenges: the scalability issue and lack of privacy.
What is a Private Version of a Public Blockchain?

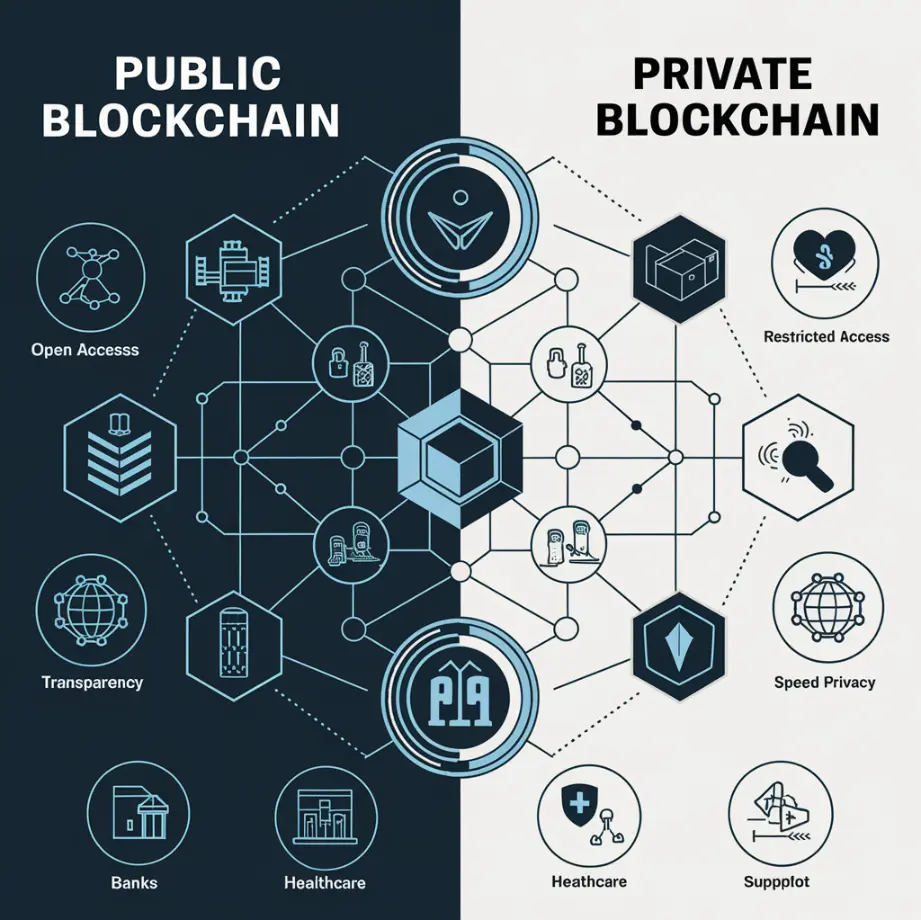
A private version of a public blockchain is a modified blockchain that retains the core features of a public blockchain but operates under restricted access. In other words, it’s a blockchain network where participation is limited to a specific group of users, such as a company, organization, or consortium.
While public blockchains are permissionless, private blockchains are permissioned. Only previously authorized users can be engaged with such a network through their consensus models, validating transactions, or accessing data. This is highly useful for businesses and institutions that require secure, confidential transactions with better control and efficiency.
Features of Private Blockchain:
- Restricted Access: Only authorized participants are allowed to enter.
- Enhanced Privacy: Transactions are visible only to authorized users.
- Faster Transaction: Since there are few participants, the network can solve complex algorithms and verify the transaction quicker.
- Rules could be changed on needs.
How Does a Private Version of a Public Blockchain Work?

A private version of a public blockchain works much like its public version, except that there are added layers of control. For example, instead of a decentralized network of miners, there might be a small group of pre-approved validators by the network administrator.
Besides, most of the private blockchains make use of consensus mechanisms like PoA or PBFT, which is highly efficient and less power-consuming compared to the Proof of Work mechanism used by public blockchains. Advantages of a Private Version of a Public Blockchain 1. Enhanced Privacy: As access is restricted, sensitive information remains confidential. 2. More Control: Organizations can implement their rules and governance structures.
- Scalability: Private blockchains can manage more transactions per second compared to public blockchains.
- Cost Efficiency: With fewer participants, transaction fees are often cheaper.
Private Blockchain Use Cases:

Private versions of public blockchains are put into use across different industries:
- Finance: Banks use private blockchains to securely and quickly transact with one another.
- Healthcare: Hospitals use these to store and share patient information securely.
- Supply Chain: Companies track the movement of goods and verify their authenticity using a private blockchain.
Difference Between Public and Private Blockchain:

Although public and private blockchains share the same foundational technology, they differ significantly in several key areas. Let’s break down these differences to better understand how each type operates.
Access:
Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open to everyone. Anyone can join the network, participate in transactions, or even validate blocks through mining. On the other hand, private blockchains restrict access to a specific group of users, such as a company or consortium. This makes private blockchains ideal for organizations that need controlled and secure environments.
Privacy:
In public blockchains, all transactions are transparent and visible to anyone on the network. While this ensures accountability, it can be a drawback for those who require confidentiality. Private blockchains, however, offer enhanced privacy by limiting transaction visibility to authorized participants only.
Speed:
Public blockchains tend to be slower due to their decentralized nature and the large number of participants involved in validating transactions. Private blockchains, with fewer participants and a more centralized structure, can process transactions much faster, making them more efficient for business use cases.
Consensus Mechanism:
Public blockchains typically use energy-intensive consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW), which require significant computational power. Private blockchains, in contrast, often rely on more efficient mechanisms like Proof of Authority (PoA) or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), which are better suited for smaller, trusted networks.
Disadvantages of Private Blockchains:
Despite such advantages, private blockchains do come with their challenges. For example, they are not as decentralized as a public blockchain and are thus susceptible to the influence of centralized control. Besides, it is expensive and resource-intensive to establish and maintain a private blockchain.
Conclusion:
So, what is a private version of the public blockchain? It is a secure, efficient, and highly customizable blockchain network for organizations needing more control and privacy. It may not offer as much decentralization compared to public blockchains, but it is a workable solution for businesses seeking to apply blockchain technology.
Whether you’re a business owner, developer, or simply a blockchain enthusiast, understanding the differences between public and private blockchains is essential. As the technology continues to evolve, private versions of public blockchains are likely to play an increasingly important role in various industries. For more information on blockchain technology, check out this guide by IBM.