Decentralization in Blockchain:
Decentralization is a fundamental concept in blockchain technology, driving its innovation and real-world applications. Decentralization simply refers to the distribution of control across a network, as opposed to its concentration in a single central entity. This article explores what decentralization in blockchain is.
What is Decentralization in Blockchain?
Decentralized identity in blockchain refers to the idea of allowing individuals to control their identity without relying on centralized authorities, like government agencies or corporations. With blockchain, users can have secure, immutable, and self-sovereign identities. These identities are stored in digital wallets, and users can selectively share or prove them without disclosing unnecessary personal information. This technology is particularly promising in sectors such as banking, healthcare, and government services, where privacy and security are paramount.
Blockchain also supports various forms of private and public blockchain networks for identity management. Learn more about the concept of Private Versions of Public Blockchain and how they work to enhance security and scalability in decentralized identity systems.
Benefits of Decentralization in Blockchain:
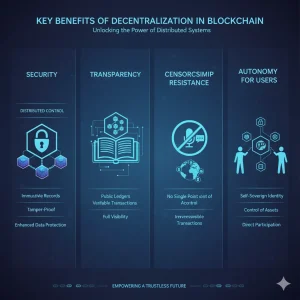
- Increased Security: No single point of failure. The distributed nature reduces the risk of hacks or fraudulent activities.
- Enhanced Transparency: Every participant can view and verify transactions, making the system open and transparent.
- Censorship Resistance: Decentralization reduces the likelihood of any government or entity censoring transactions.
- Autonomy for Users: It empowers users to control their assets, data, and identity without relying on third parties.
Some popular decentralized technologies and tools related to blockchain include Ethereum, Bitcoin, and the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), all of which utilize decentralization as a fundamental feature.
Types of Decentralization in Blockchain:

There are several types of decentralization that can occur within blockchain networks:
- Network Decentralization: This type refers to the distribution of the nodes (computers) in a blockchain network. More nodes mean higher decentralization, as no single node can control the entire network.
- Protocol Decentralization: Protocol decentralization ensures that the decision-making process for changes in the protocol is distributed across the network, rather than being governed by a central entity.
- Application Decentralization: In decentralized applications (dApps), users can access services without needing to trust any centralized entity. The applications run on decentralized networks, ensuring that control remains distributed.
Decentralized Applications (dApps) in Blockchain:
Decentralized applications, or dApps, are built on blockchain technology and function without a central governing authority. These applications leverage blockchain technology to guarantee the decentralization of all data, transactions, and processes. For example, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms like Uniswap allow users to trade digital assets peer-to-peer, removing the need for traditional intermediaries such as banks. dApps are gaining traction across industries, from finance to gaming, due to their security, transparency, and resilience.
Decentralization in dApps also drives some of the advantages of blockchain technology, such as lower transaction fees and faster processing times. Learn more about the Advantages of Blockchain and how they contribute to the growth of dApps. Yes, Chromebooks can be great for students, especially those in need of a budget-friendly, lightweight, and secure device for everyday tasks. They work well for research, email, and basic productivity tasks like word processing or spreadsheets. However, for students who require specialized software or higher processing power, laptops might be the better option.
If you’re interested in more comparisons between Chromebooks and other high-end devices, check out our article on Chromebook vs MacBook: Which One is Better? to explore the pros and cons of Chromebooks and MacBooks, which are two popular choices for students.
What is Decentralized Identity in Blockchain?
Decentralized identity in blockchain refers to the idea of allowing individuals to control their own identity without relying on centralized authorities, like government agencies or corporations. With blockchain, users can have secure, immutable, and self-sovereign identities. These identities are stored in digital wallets, and users can selectively share or prove them without disclosing unnecessary personal information. This technology is particularly promising in sectors such as banking, healthcare, and government services, where privacy and security are paramount.
Benefits of Decentralized Identity in Blockchain:
- Privacy and Security: Users maintain control of their personal data and can avoid unnecessary sharing of sensitive information.
- Portability: Decentralized identities are portable, meaning users can take them across various services without worrying about losing access to their identity.
- Reduced Fraud: By using blockchain’s immutable nature, fraudulent activities related to identity theft can be minimized.
Decentralized Technologies in Blockchain:
Blockchain closely correlates with the rise of decentralized technologies. These technologies, such as distributed ledgers, smart contracts, and cryptographic protocols, enable peer-to-peer interactions without intermediaries. Some well-known decentralized technologies include:
- Ethereum: A blockchain platform that supports decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts.
- IPFS: A protocol for storing and sharing files in a decentralized manner.
- Hyperledger: A blockchain framework for businesses to build decentralized solutions.
These technologies are transforming industries, enabling more secure, transparent, and efficient systems without relying on centralized control.
FAQs:
Could you please explain what decentralization in blockchain entails?
Decentralization in blockchain refers to distributing control and decision-making across a network of participants, rather than having it centralized in one entity.
How does decentralization in blockchain benefit the financial industry?
Decentralization allows peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, leading to faster, cheaper, and more secure financial systems.
What are the different types of decentralization in blockchain?
The main types of decentralization include network decentralization, protocol decentralization, and application decentralization.
What is decentralized identity in blockchain?
DeCentralized identity allows individuals to manage their personal data, which is stored on the blockchain, without depending on centralized authorities.
How do decentralized applications (dApps) work?
dApps run on decentralized networks, ensuring transparency, security, and autonomy for users without relying on central servers.
What decentralized technologies are used in blockchain?
Technologies such as Ethereum, IPFS, and Hyperledger support the development of decentralized applications, smart contracts, and distributed file storage.